About
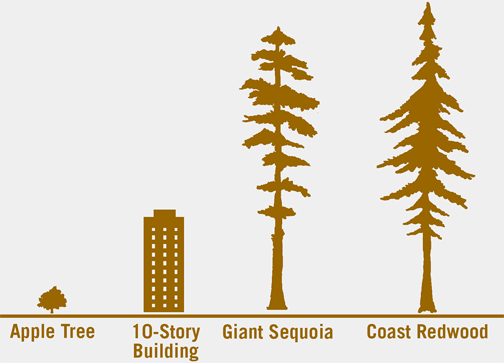
Standing at the base of Earth’s tallest tree, the coast redwood, is one of life’s most humbling and amazing experiences. These California trees can reach higher than a 30-floor skyscraper (more than 320 feet), so high that the tops are out of sight. Their trunks can grow more than 27 feet wide, about eight paces by an average adult person! Even more incredible: These trees can live for more than 2,000 years. Some coast redwoods living today were alive during the time of the Roman Empire.
History
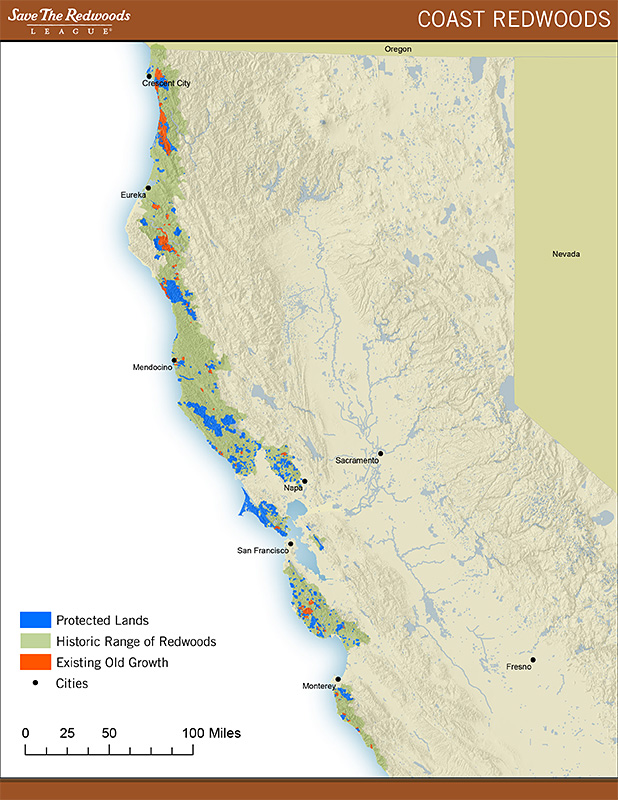
Redwoods once grew throughout the Northern Hemisphere. The first redwood fossils date back more than 200 million years to the Jurassic period. Before commercial logging and clearing began in the 1850s, coast redwoods naturally occurred in an estimated 2 million acres (the size of three Rhode Islands) along California’s coast from south of Big Sur to just over the Oregon border. When gold was discovered in 1849, hundreds of thousands of people came to California, and redwoods were logged extensively to satisfy the explosive demand for lumber and resources. Today, only 5 percent of the original old-growth coast redwood forest remains, along a 450-mile coastal strip. Most of the coast redwood forest is now young. The largest surviving stands of ancient coast redwoods are found in Humboldt Redwoods State Park, Redwood National and State Parks and Big Basin Redwoods State Park.
The native people of California did not typically cut down coast redwoods, but used fallen trees to make planks for houses and hollowed out logs for canoes.

You must be logged in to post a comment.